The gas is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and its temperature drops to 450 K at the exit. CO_2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of the CO_2 drops to 450k at the exit.
Solved 6 Carbon Dioxide Gas Enters A Pipe At 3 Mpa And 500 Chegg Com
The gas constant the critical pressure and the critical temperature of CO2 are R 01889 kPa mkg K.

. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of the CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit.
Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2kgs. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the. Problem 89 Easy Difficulty.
Mechanical Engineering QA Library - Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe with a flow rate of 219 kgs at a pressure of 37 MPa and cools at a constant pressure as it travels through the pipe reaching a temperature of 440 K at the outlet. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs.
Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized compressibility chart. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of CO2 at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized compressibility chart. Carbon dioxide gas enters a turbine at 5 MPa 100 C and exits at 1 MPa.
CO 2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO 2 drops to 450 K at the exit. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500k at a rate of 2 kgs. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe usinga the ideal gas equation and b the generalized compressibility chart.
C O 2 CO_2 C O 2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of C O 2 CO_2 C O 2 drops to 450 K at the exit. If CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe so that the temperature of CO2 drops to 450 K at. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized.
Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Carbon dioxide molecules consist of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.
CO 2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO 2 drops to 450 K at the exit. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit.
Carbon dioxide gas at 3 MPa and 500 K flows steadily in a pipe at a rate of 04 kmols. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs.
Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 k g s. A The ideal-gas equation and bThe generalized compressibility chart. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of the CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit.
Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using.
C O 2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of the C O 2 drops to 450 K at the exit. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3MPa and 500K at a rate of 2kgs.
Tc 3042 K and Pc 739 MPa. Determine a the volume and mass flow rates and the density of carbon dioxide at this state. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b.
CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit. TextCO_2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of the textCO_2 drops to 450 K at the exit. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit.
Determine a the volume and mass flow rates and the density of carbon dioxide at this state. Carbon dioxide chemical formula CO 2 is a chemical compound occurring as an acidic colorless gas with a density about 53 higher than that of dry air. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using.
Carbon dioxide gas at 3 MPa and 500 K flows steadily in a pipe at a rate of 04 kmols. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and b the generalized.
CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit. It occurs naturally in Earths atmosphere as a trace gasThe current concentration is about 004 412 ppm by volume. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit.
Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using. Which of the following is the volumetric flow rate at the outlet when carbon dioxide gas is considered an ideal gas. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs.
CO 2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature of CO 2 drops to 450 K at the exit. If the isentropic efficiency of the turbine is 75 determine the exit temperature and the second-law efficiency. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe and the temperature CO2 drops to 450K at the exit.
Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using the ideal gas equation. Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxide at the inlet and the volume flow rate at the exit of the pipe using a the ideal-gas equation and.
Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kgs. Find step-by-step Engineering solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.

Solved Carbon Dioxide Gas Enters A Pipe At 3 Mpa And 500 K1 Chegg Com

Solved Carbon Dioxide Gas Enters A Pipe At 3 Mpa And 500 K Chegg Com
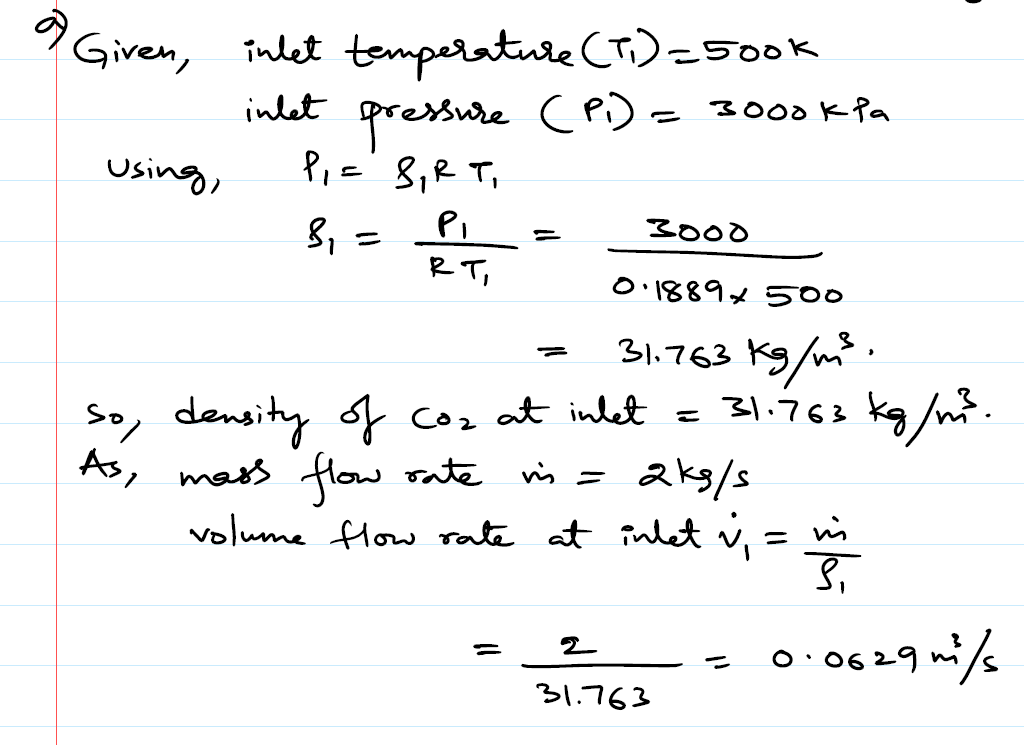
Answered Carbon Dioxide Gas Enters A Pipe At 3 Bartleby

Solved Carbon Dioxide Gas Enters A Pipe At 3 Mpa And 500 K Chegg Com
0 Comments